Rapid Fire Abstracts
Fetal Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking Myocardial Strain Analysis in Congenital Heart Disease (RF_FR_317)
- TV
Thomas M. Vollbrecht, MD
Physician
University Hospital Bonn, Germany - TV
Thomas M. Vollbrecht, MD
Physician
University Hospital Bonn, Germany - CH
Christopher Hart, MD
Pediatric Cardiologist
University Hospital Bonn, Germany - AI
Alexander Isaak, MD
Attending Physician
University Hospital Bonn, Germany - UA
Ulrike Attenberger, MD
Physician
University Hospital Bonn, Germany - AG
Annegret Geipel, MD
Prenatal Medicine Specialist
University Hospital Bonn, Germany - BS
Brigitte Strizek, MD
Physician
University Hospital Bonn, Germany 
Julian A. Luetkens, MD
Physician
University Hospital Bonn, Germany
Presenting Author(s)
Primary Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) is an emerging imaging modality for assessing anatomy and function of the fetal heart in congenital heart disease (CHD). This study aimed to evaluate myocardial strain using fetal CMR feature tracking (FT) in different subtypes of CHD.
Methods:
Fetal CMR FT analysis was retrospectively performed on four-chamber cine images acquired with Doppler US gating at 3 Tesla. Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS), LV global radial strain (GRS), LV global longitudinal systolic strain rate (SR), and right ventricular (RV) GLS were quantified using a dedicated software optimized for fetal strain analysis. Analysis was performed in normal fetuses and different CHD subtypes (d-Transposition of the great arteries (dTGA), hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS), coarctation of the aorta (CoA), tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), RV-dominant atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD), and critical pulmonary stenosis or atresia (PS/PA)). Analyses of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey post-hoc test was used for group comparisons.
Results:
A total of 60 fetuses were analyzed (8/60 (13%) without CHD, 52/60 (87%) with CHD). Myocardial strain was successfully assessed in 113/120 ventricles (94%). Compared to controls, LV GLS was significantly reduced in fetuses with HLHS (-18.6±2.7% vs. -6.2±5.6%; p< 0.001) and RV-dominant AVSD (-18.6±2.7% vs. -7.7±5.0%; p=0.003) and higher in fetuses with CoA (-18.6±2.7% vs. -25.0±4.3%; p=0.038). LV GRS was significantly reduced in fetuses with HLHS (25.7±7.5% vs. 11.4±9.7%; p=0.024). Compared to controls, RV GRS was significantly reduced in fetuses with PS/PA (-16.1±2.8% vs. -8.3±4.2%; p=0.007). Across all strain parameters, no significant differences were present between controls and fetuses diagnosed with dTGA and TOF.
Conclusion:
Fetal myocardial strain assessment with CMR FT in CHD is feasible. Distinct differences are present between various types of CHD, suggesting potential implications for clinical decision-making and prognostication in fetal CHD.
Bar plots showing strain measurements across different CHD subgroups and for normal control fetuses. AVSD = atrioventricular septal defect; CoA = coarctation of the aorta; dTGA = d-transposition of the great arteries; HLHS = hypoplastic left heart syndrome; LV = left ventricle; PS/PA = pulmonary stenosis/atresia; RV = right ventricle; TOF = tetralogy of Fallot.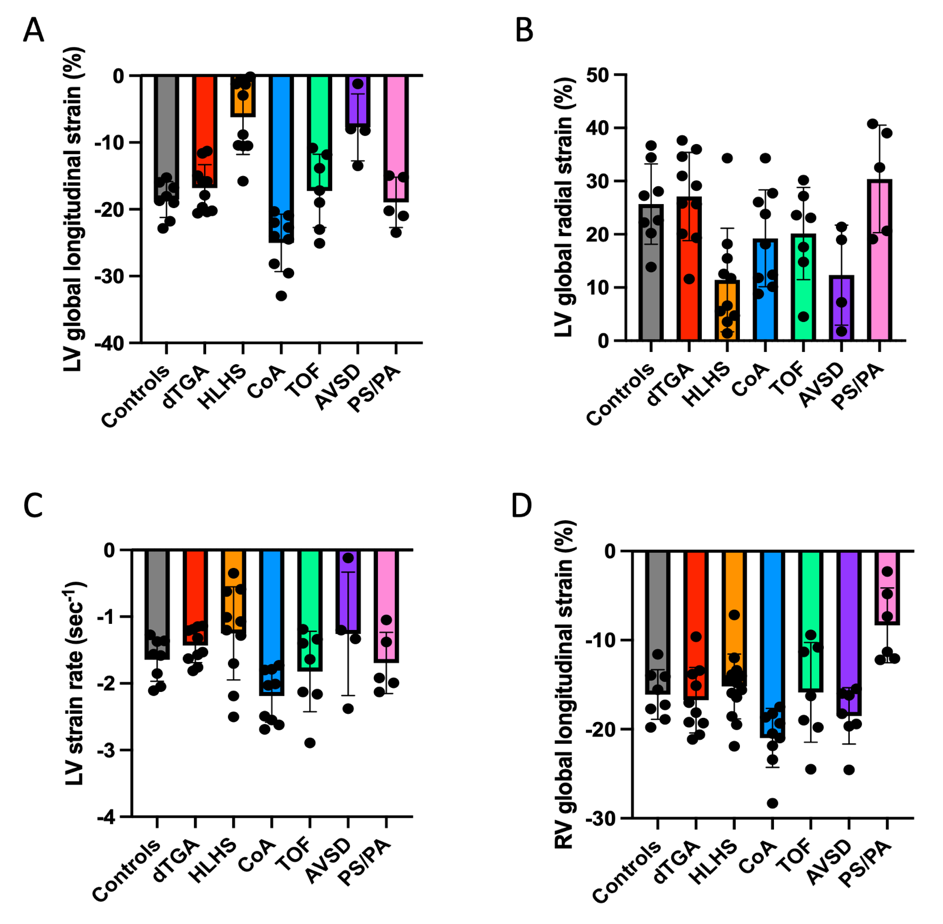
Scatter plot showing left (LV) and right ventricular (RV) global longitudinal strain measurements in individual fetuses with congenital heart disease and normal control fetuses. A wide range of LV and RV global longitudinal strain values were present across different CHD entities with considerable overlap with normal values particularly in fetuses with d-transposition of the great arteries and tetralogy of Fallot.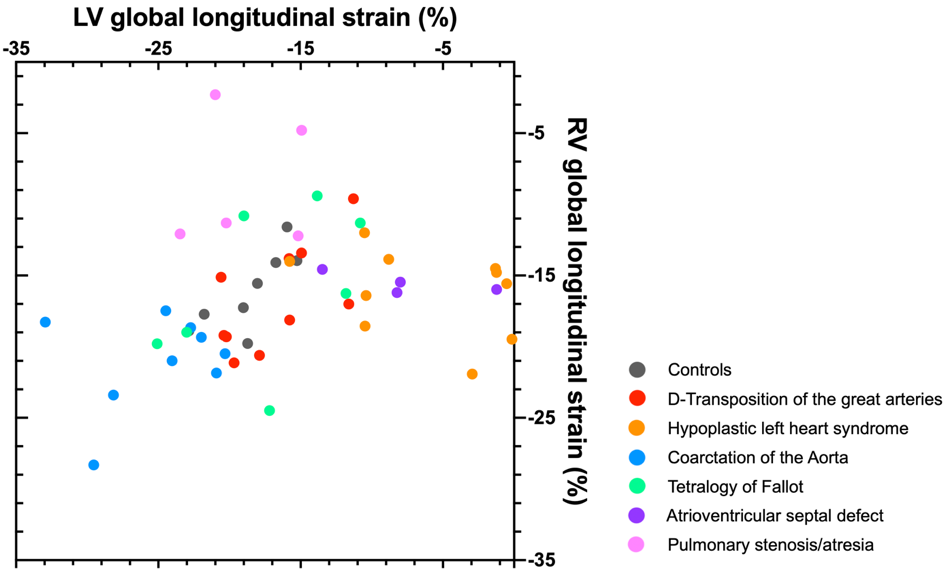
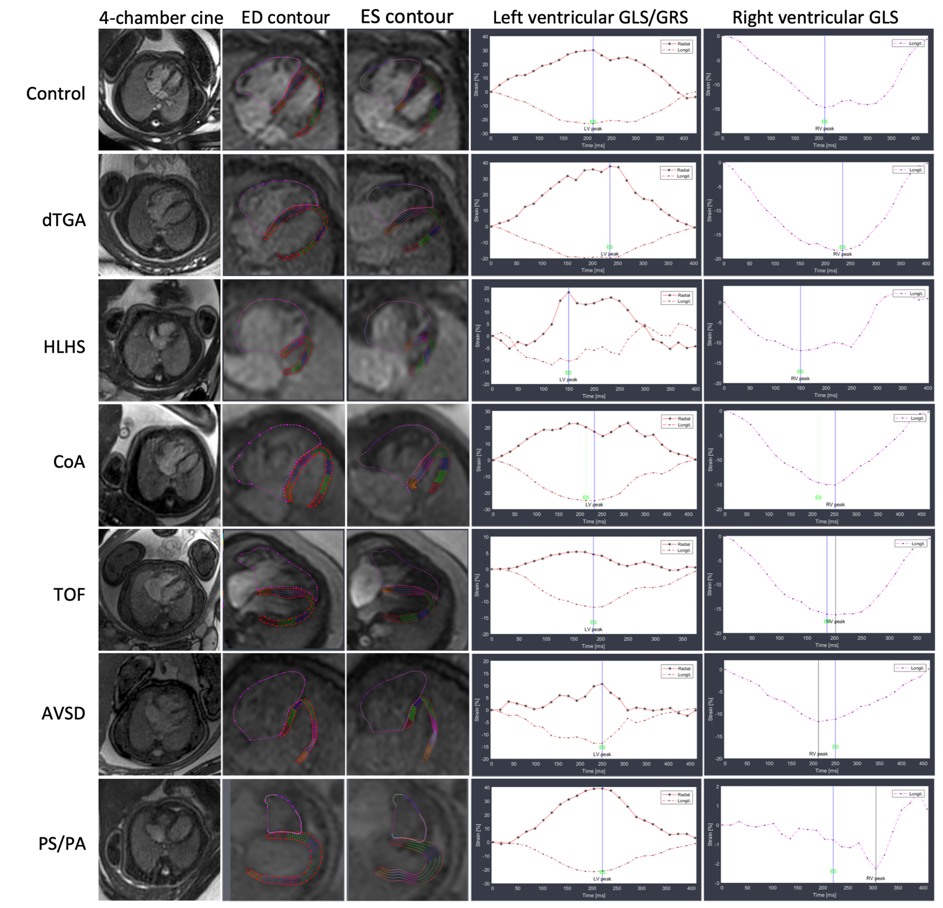
Left and right ventricular strain measurements displayed as curves across the cardiac cycle of different CHD entities including corresponding end-diastolic (ED) and end-systolic (ES) endocardial border contours. Please note that the hypoplastic left ventricle in the fetus with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS), the left ventricle in the fetus with right ventricular-dominant atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD), and the right ventricle in the fetus with pulmonary stenosis/atresia exhibit irregular deformity patterns over the cardiac cycle, diverging from the typical strain curves observed in the other fetuses. CoA = coarctation of the aorta; dTGA = d-transposition of the great arteries; ED = end-diastolic; ES = end-systolic; GLS = global longitudinal strain; GRS = global radial strain; TOF = tetralogy of Fallot.