Oral Abstract
Effect of metformin on myocardial fibrosis and cardiac function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a longitudinal cohort study using cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- XZ
Xinyuan Zhang, Dr
Doctor
Department of Radiology, Key Laboratory of Obstetric and Gynecologic and Pediatric Diseases and Birth Defects of Ministry of Education, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, 20# Section 3 South Renmin Road, Chengdu 610041, China, China (People's Republic) - XZ
Xinyuan Zhang, Dr
Doctor
Department of Radiology, Key Laboratory of Obstetric and Gynecologic and Pediatric Diseases and Birth Defects of Ministry of Education, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, 20# Section 3 South Renmin Road, Chengdu 610041, China, China (People's Republic) - YG
Yingkun Guo, PhD
Dr
West China Second University Hospital, China (People's Republic) 
Huayan Xu, PhD
Doctor
West China Sencond University Hospital, Sichuan University, China (People's Republic)
Presenting Author(s)
Primary Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: This observational cohort study included patients with DMD who received metformin regularly and underwent two cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) studies with one-year interval between July 2018 and June 2023. The same number of age-matched patients with DMD who had never received metformin as a control group. The primary outcome was late gadolinium enhancement accumulation progression from baseline to follow-up CMR. The second outcome was the left ventricular ejection fraction change between the two CMRs. After adjusting for confounding factors, we used a multivariate generalized linear regression model (GLM) to assess the association between baseline variables and outcomes.
Results:
A total of 43 boys (median=9.0 years) as metformin group and 43 boys (median=8.0 years) as control group were included in the study. After a median follow-up of 12.0 and 12.6 months, 17 (39.5%) and 19 (44.2%) participants in the metformin and control cohorts reached the outcome of MF progression, respectively. Additionally, 23 (53.5%) and 35 (81.4%) participants reached the cardiac function progression endpoint, respectively. Among patients receiving cardiac medications without cardiac dysfunction, MF progression increased significantly in the control group (10.94% [IQR: 7.75 to 13.30%], P=0.018) but not in the metformin group (1.60% [IQR: -0.91 to 5.07%], P=0.260). Similar findings were observed in the progression of cardiac function in patients without left ventricular dysfunction, regardless of cardiac medications use. Multivariate GLMs, adjusted for confounding factors, showed that metformin use was independently associated with myocardial fibrosis and cardiac function progression.
Conclusion: Early metformin therapy before cardiac dysfunction, initiated with good myocardial conditions, seems to benefit patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. These effects encourage further large-scale investigations of DMD and aid clinicians in providing early additional interventions for patients.
Overview of study methodology and findings. LGE= late gadolinium enhancement; LVEF= left ventricular ejection fraction. 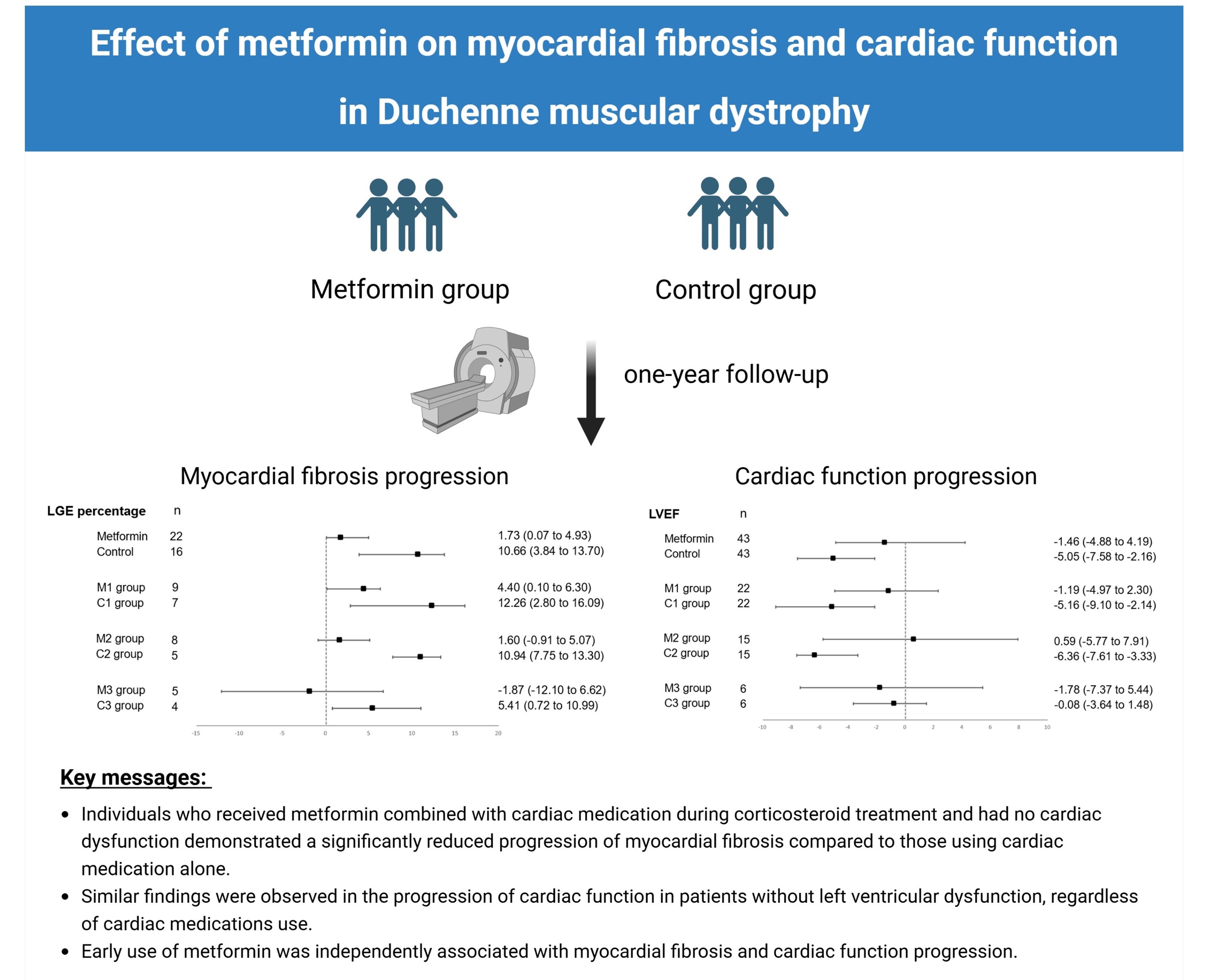
Flowchart of the study. Abbreviations: CMR= cardiac magnetic resonance; LVEF= left ventricular ejection fraction. 

